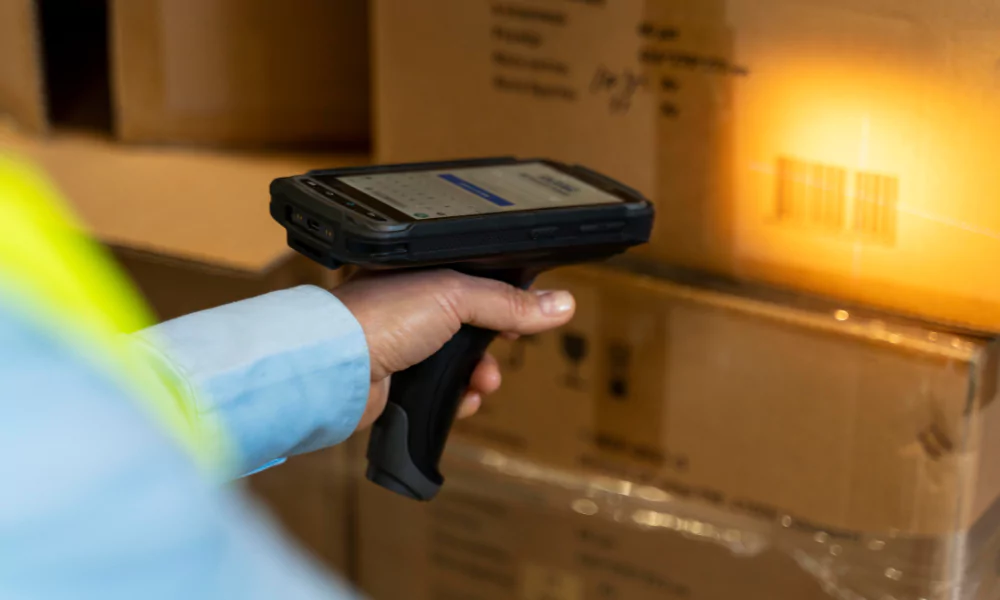

Unlocking the future of innovation, RFID technology emerges as a strategic cornerstone, aligning seamlessly with corporate objectives. From trimming production costs to elevating customer relationships and streamlining operations, RFID holds the key to transformative success.
In the realm of manufacturing, a shared pursuit of efficiency finds a powerful ally in RFID. Designed for precision, it facilitates product tracking across lifecycles, enables data-driven logistics analysis, and optimises production flows.
Join us in exploring the components, advantages, and market outlook of RFID, delving into the pulse of its latest trends and innovations. Uncover the promising landscape shaped by RFID future trends.
Introduction to RFID:
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) is a wireless communication technology designed to identify and track objects through the transmission of specific serial numbers. As a form of Auto-ID software, RFID serves to streamline processes, reduce time and labour, and enhance real-time data accuracy.
The fundamental component of RFID is the inventory tag, typically consisting of a microchip connected to a radio antenna. This tag is affixed to objects, linking them to the internet for future reference and enabling data exchange with businesses across the supply chain.
There are two primary types of RFID devices: passive and active. Passive RFID labels lack transmitters but reflect radio signals from reader antennas. On the other hand, active RFID devices, also known as transponders, contain a microchip with an antenna and actively transmit data to a reader, relaying the information to a computer.
RFID technology finds extensive use in tracking significant assets such as freight boxes, rail cars, or containers, particularly when long-distance transportation is involved. Passive RFID tags, being energy-efficient and transmitter-free, require minimal maintenance and are a cost-effective alternative to RFID tags.
Advantages of RFID:
RFID systems are capable of keeping your data secure and are equipped to read data. Additionally, they have a few other advantages, let’s read about them below:
1. Compact Size:
The compact size of RFID cards, similar to regular bank cards, makes them easy to store and carry. This minimizes the chances of users forgetting their access cards when heading to locations requiring access. The portability and handiness of RFID cards contribute to their widespread adoption.
2. Versatility and Adaptability:
RFID locks come with various ranges of cams and spindle lengths, catering to a wide array of doors and furniture types. This versatility makes RFID technology suitable for diverse business applications, ensuring compatibility with different access points and environments.
3. Master Card Functionality:
A notable advantage of RFID technology lies in its master card functionality. Different locks can be programmed to recognize and accept a single RFID key card, eliminating the need for multiple cards for various locks. This not only simplifies access management but also allows each lock to maintain independent access policies.
4. Enhanced Security:
RFID systems offer a high level of security as specialized equipment is required to read the data stored on RFID tags. This inherent security feature contributes to maintaining the integrity of lock systems, making unauthorized access more challenging.
5. Convenience and Speed:
RFID technology provides unmatched convenience and speed in access control. With just a fraction of a second required to place an RFID key in proximity to unlock a security system, the process is not only swift but also highly convenient for users, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Diverse Applications of RFID:
RFID is seamlessly woven into daily life, often unnoticed. From unlocking hotel doors to pet microchips, its applications span industries globally.
1. Aerospace & Defence
In Aerospace and Defence, the last decade witnessed a strategic adoption of RFID technologies in crucial processes. Airframers capitalize on RFID to meticulously track numerous aeroplane components, fortifying their supply chain.
Automation and error reduction in key areas, including Supply Chain, Manufacturing, and Maintenance & Repair, yield substantial returns, enhancing operational efficiency for industry leaders.
2. Medical
RFID’s transformative impact on healthcare extends across operations, systems, and personnel management, fostering efficiency and precision. Mark Roberti, founder of the RFID Journal, notes the potential for cost reduction in healthcare by avoiding redundant purchases.
This RFID-assisted revolution is not only enhancing processes but also contributing to saving lives in the healthcare industry.
3. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
In the realm of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), businesses are rapidly embracing connectivity, particularly in manufacturing for heightened productivity. IIoT facilitates comprehensive data organization, analysis, and documentation throughout the product lifecycle.
RFID readers enable real-time identification, tracking, and monitoring, fostering industry-wide collaboration. The integration of 5G enhances voice and data communications, ensuring faster and more reliable supply chain management.
This interconnected system allows diverse devices to share information, enabling insightful, data-driven decisions, such as managing energy, security, and lighting in both homes and workplaces.
RFID Future Trends:
As we witness ongoing developments in RFID and barcoding, there’s an anticipation for an array of additional applications to emerge in the near future. The landscape is evolving, and we eagerly anticipate the realization of these solutions, adding further excitement to the already dynamic realm of RFID and barcoding advancements.
Let’s look at some future trends in RFID:
1. Increased Sustainability Measures:
RFID technology will align with sustainability goals, with a focus on developing eco-friendly tags and solutions. The industry will explore materials and manufacturing processes that reduce environmental impact. Sustainable RFID applications will contribute to a more responsible and environmentally conscious use of technology.
2. Flexible Printing Options:
Harnessing high-performance thin-film transistor technology, today’s RFID tags are remarkably thinner and more flexible than previously envisioned. This innovation allows them to seamlessly adhere to diverse surfaces.
Integrating RFID into a bend-resistant, flexible substrate expands its applications, overcoming previous limitations in settings with physical constraints.
3. Integrations with Other Technologies:
Today’s RFID tags boast versatility and emerging integrations propel them to new heights. Current warehouse management systems leverage RFID for enhanced traceability, precision in picking, and efficient delivery.
Looking ahead, the integration of smart-sensing RFID into the Internet of Things (IoT) will revolutionize warehouses by tracking various factors, including temperature, for optimized supply chain operations.
4. Cloud-Based Data Storage:
RFID’s enduring advantage lies in mobility, a facet set to evolve with the integration of cloud-based data storage into future systems. Storing real-time data in the cloud enhances accessibility, optimizing stock accuracy, product availability, and replenishment. This streamlining benefits supply chain processes, boosting productivity and accuracy across teams.
5. More Innovative Applications:
Beyond the highlighted materials and technologies, RFID trends will advance as industry leaders innovate for optimal solutions. These systems are increasingly recognized as interconnected solutions, encompassing various applications and readers.
Future accessibility extends beyond warehouses and healthcare, envisioning consumers installing personal RFID readers at home for seamless integration with management systems and IoT devices.
Market Outlook:
1. Growing Adoption Across Industries:
RFID technology is gaining prominence as an alternative identification system, particularly in challenging environments. Industries are increasingly recognizing its potential for diverse applications.
2. Innovative Tamper-Proof RFID Labels:
Identiv’s creation of a Tamper-Proof RFID label showcases advancements in security. The label’s data carrier erases information upon removal, addressing security concerns and preventing unauthorized access to company data.
3. Printed Sensors Integration:
Integration of printed sensors onto RFID smart labels marks a significant development. The inkjet-printed multi-sensing platform on flexible substrates, incorporated into high-frequency RFID smart labels, offers capabilities like humidity, ammonia, and temperature detection simultaneously.
4. Cost-Effective Manufacturing:
The inkjet printing technology allows flexible plastic surfaces, reducing manufacturing costs. RFID smart labels deliver information gathered by readers from integrated sensors, enhancing environmental monitoring in the supply chain, especially in the food industry.
Key RFID innovations
1. Sensor-Enabled RFID Tags:
Tags with built-in temperature, humidity, or shock sensors for monitoring sensitive goods.
2. Paper-Based & Eco-Friendly Tags
Sustainable RFID inlays made from recyclable materials to reduce environmental impact.
3. Energy-Harvesting Tags
Self-powered tags that capture energy from RFID readers or the environment, eliminating batteries
4. Integration with AI & IoT
Smart RFID networks that use AI for predictive analytics and IoT for real-time tracking.
5. Blockchain-Linked RFID
Secure, tamper-proof tracking for high-value goods like pharmaceuticals and luxury items.
Conclusion
In conclusion, RFID technology stands at the forefront of innovation, seamlessly aligning with corporate objectives and reshaping industries. From manufacturing efficiency to healthcare advancements, RFID’s transformative influence is evident.
As we anticipate RFID future trends, including sustainability measures and flexible printing options, the horizon of possibilities expands. The integration of RFID into everyday life, coupled with market projections, emphasizes its pivotal role in the evolving technological landscape.
Embrace the future with Qodenext, your partner in unlocking the potential of RFID technology and staying ahead in this era of dynamic advancements and connectivity. RFID future trends await, and Qodenext is here to guide you through this exciting journey.
FAQ: RFID Future Trends and Innovations
1. What are the disadvantages of RFID technology?
RFID’s disadvantages include potential privacy concerns, initial implementation costs, and susceptibility to interference or hacking. Compatibility issues and the need for standardization are also challenges.
2. Can RFID be reused?
RFID tags can be reusable, especially passive ones. However, it depends on the type and design. Active RFID tags with batteries may have a limited lifespan.
3. What are the limits of RFID?
RFID has limitations in reading range, requiring close proximity. It can be affected by metal and liquids, impacting signal strength. Additionally, initial costs and security concerns pose challenges.
4. Can RFID tags be blocked?
RFID tags can be blocked or shielded using materials like metal or foil. This prevents them from responding to reader signals, enhancing privacy or security in certain scenarios.
5. What are the key future trends in RFID technology?
Future RFID trends include integration with IoT and AI, development of flexible and printed RFID tags, enhanced security features, ultra-high-frequency (UHF) RFID adoption, and the rise of smart sensor-enabled tags.
6. How will RFID integrate with other emerging technologies?
RFID will work closely with the Internet of Things (IoT) to enable real-time tracking and condition monitoring, while AI will provide advanced analytics for predictive maintenance and smarter decision-making across supply chains.
7. What innovations are expected in RFID tag design?
Innovations include ultra-thin, bendable tags created using printed electronics, battery-less sensors for environmental monitoring, and the use of blockchain for secure and tamper-proof data recording.
8. How is RFID contributing to sustainability efforts?
RFID advancements focus on eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes, reducing waste through better inventory accuracy, and enabling sustainable supply chain practices by minimizing overproduction and spoilage.
9. What industries are leading RFID adoption and innovation?
Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, aerospace, logistics, retail, and agriculture are rapidly adopting and innovating with RFID technologies to enhance tracking, security, and efficiency.
10. What are the challenges currently facing RFID technology?
Challenges include privacy concerns, initial implementation costs, interference issues (especially around metals and liquids), the need for standardization, and cybersecurity threats.






