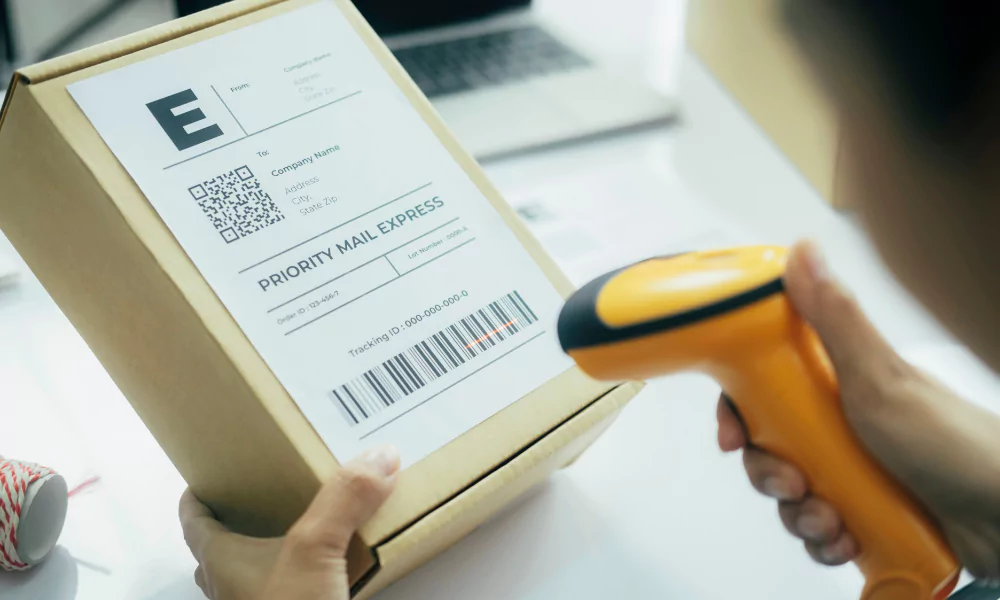
Have you ever noticed a cashier in a mall or supermarket? If yes, then You will usually notice him scanning purchases made by customers with the help of a laser device. Did it ever cross your mind why is the cashier doing so? Well, he is scanning the Barcodes of a product to generate the bill. With technological development all around us, Barcode technology has become an essential part of making cashless transactions, managing inventory, and structuring business operations.
This blog will help you understand its functionalities and benefits.
Let’s explore!
Barcode – What Is It?
A barcode is a predefined set of black bars and white spaces whereas a barcode technology is an automatic identification technology that uses barcodes.
These codes usually have a hidden message or information encoded in it that can only be retrieved with the help of a scanner connected to a computer.
Each barcode has specific information which can only be understood by computers. This helps in keeping things organized.
How Does A Barcode Work?
Barcode technology requires various components like a barcode scanner and a sensor to work efficiently.
- The black and white lines denote different kinds of letters and numbers. When you scan the barcode with a scanner it reads these lines and turns into a text that’s readable and understandable.
- Scanner machines are a crucial part of decoding hidden messages quickly. A light is required to shine on the barcode, an automatic sensor to detect the light bouncing back, and a decoder to translate the useful information encoded into it.
- Once the scanning process is done the information is sent to the computer. It searches the database to find that specific barcode and shows the information related to the product.
To scan the product you just point the scanner at the barcode and press a button.
Now let’s move on to knowing about the different types of Barcode Technology.
What Are Its Types
Basic Barcodes are usually of two types;
1. Linear or 1D Barcodes
Linear or 1D barcodes are the traditional black vertical bars that have numbers beneath them which is commonly seen in stores.
These codes hold information related to the product like name, colour, size, and type in a database. They are used basically on consumer goods, shipping labels, or books.
2. Matrix or 2D barcodes
Matrix or 2D barcodes are usually like QR codes that store additional information other than traditional barcodes.
They can contain information related to quantity, web links, and images without any requirement of a database.
These codes are handy in the pharmaceutical industry where there is a need for precise tracking of medical equipment.
Though basic barcodes are of two types, when discussing the product barcodes, there are 4 common types of it. Want to know about it? Read further to understand.
Four Common Product Barcodes
Product barcodes play an essential role in identifying the products in the businesses. Most commonly used barcodes are:
1. UPC Barcodes
UPC Barcode also known as universal product code is used worldwide in the retail sector to scan and label the product.
They come into main types UPC-A with 12 digits and UPC-E with 6 digits. These codes help in the identification of the product in a quick manner
2. MSI Plessey
These barcodes only hold numbers but can take a long time to store huge amounts of data. However, they are not as efficient as the new codes which are cost-effective.
3. EAN barcode
EAN barcodes are used worldwide for scanning consumer goods, especially in Europe. EAN-8 has eight digits suitable usually for small items whereas EAN-13 has 13 digits usually suitable for larger data. They are quite adaptable.
4. Code 39
These barcodes are commonly used in industries like defence and automotive. They can encode both characters and numbers and were initially limited to only 39 characters but now it expanded to 43.
Now we know exactly how barcode technology works and its types in brief but do we know where these codes are used?
Let’s find out!
Where Do We Use It?
Barcodes are mainly used for business operations in various industries.
It is a surprising fact that some of the industries cannot function without barcode technology.
Some of its common applications are-
Air Travel where it is used for purposes like ticketing, check-in process, lounge access, etc.
Retail Outlets where it is used for scanning the QR code on the items they want to purchase and making the payment within seconds.
Hospitals where it is used to check the authenticity of medicines. Barcodes can be used to provide detailed information about medicines. This ensures the safety of patients and resolves compliance issues.
Having known its applications, it is necessary to understand why we use Barcode Technology and its benefits
Let’s delve further into it!!
Benefits and Uses
Barcodes can be used in uncountable ways as they improve the efficiency of the daily operations of businesses. Given below are some of the most popular uses and benefits of it.
1. For maintaining accuracy
Barcode eliminates the scope of error as there is no requirement for manual entry of information related to the product.
Be it warehouses or retail stores, you can simply swipe the scanner on the barcode. Error in barcodes is a rare case.
2. Inventory management
Managing inventory is a crucial part of business as it involves tracking inventory. This allows employees to review the positions of inventories which facilitates them to make improved decisions around purchases.
3. Up-to-date Data
Every single time when a barcode is scanned, it immediately updates the sales numbers and the inventory in the company’s business management system.
Businesses can easily get access to the real-time allowing them to make calculations.
4. Cost-effective
Barcodes are of immense value as the amount of investment required as compared to complicated systems is much less
Many companies create their barcodes for internal use at a minimal price and the cost of technology is affordable.
Barcode Technology In The Warehouse Management System.
Efficiency in warehouses requires moving huge containers and products smoothly through various Unique steps. Using manual data entry can lead to errors and might be time-consuming. Here warehouse barcodes come to the rescue.
The whole warehouse barcode scanning process has various steps. To get a detailed view of it read below,
Step 1-Selecting an Appropriate Barcode Scanner
Choosing the correct hardware that is compatible with your system and meets the warehouse’s needs is an important factor. Other factors that need to be kept in check are connectivity, battery life, the distance with which the product will be scanned, and durability.
Step 2- Choosing the Symbologies.
Warehouse associates need to decide the type of barcode to be designed. Whether it should be a linear barcode or a 2D barcode whichever suits the inventory. Common options include UPC Barcodes, EAN, MSI Plessey, etc.
Step 3- Designing Barcode Labels.
Labels are of various types which include multi-level, single-level, container label, floor labels, etc. Factors that need to be kept in check while designing a barcode are its size, material, and the method of attachment.
Step 4- Establishing the Whole Barcode Process
Ensuring the implementation of the procedures in the correct manner by applying the labels, updating the information in the system, and scanning items is crucial.
By following all the above steps, A warehouse can efficiently track inventory leading to accuracy and increased productivity.
FAQ: Everything You Need To Know About Barcode Technology
What is a Barcode Scanner?
A Barcode scanner is a kind of barcode reader that decodes messages and is an essential part of barcodes technology.
How to generate a Barcode?
Barcodes are usually generated by using software. One needs to decide what information they want to add to the barcode and select a barcode format. Software easily generates codes that are understandable by machines.
Can I create my Barcode?
You can create your barcodes with the help of any free barcode generator available online. This is the easiest way to create your barcodes.
Conclusion
Barcode technology offers warehouses a structured and productive way to manage inventory. By implementing barcode system warehouses, the companies can easily track the real-time data, reduce errors and save their own time.
To implement proper processes in place, Qodenext is one such solution that may improve the overall efficiency, and profitability and optimize your business operations. Their printing solutions are reliable and serve a wide variety of industries.