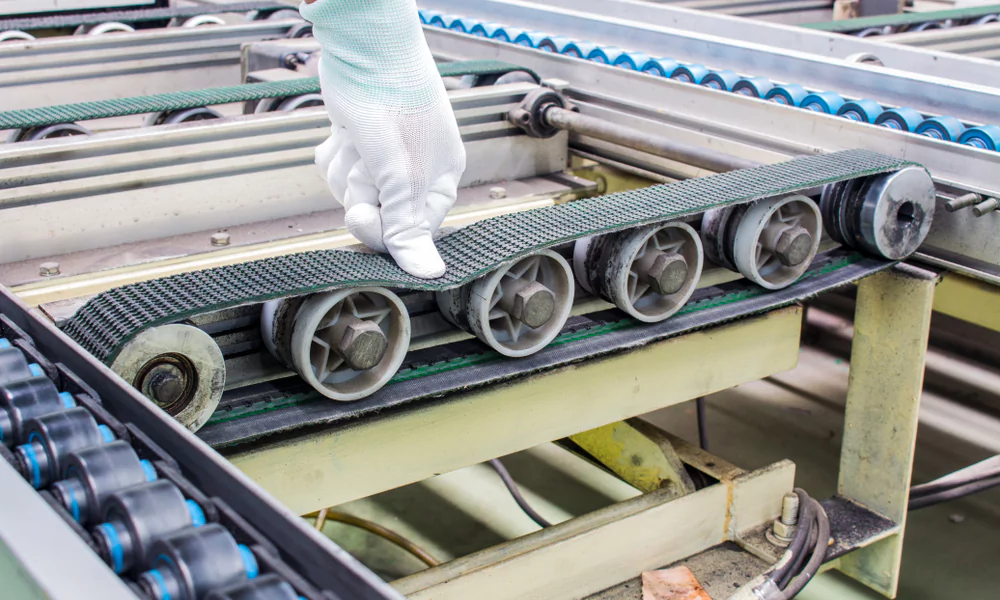
In the bustling environment of modern factories and industries, conveyor belt silently bear the weight of production, ensuring the seamless movement of materials. Yet, neglecting their maintenance can lead to costly disruptions, from breakdowns to operational inefficiencies.
Given their critical role, it’s paramount to prioritize proper care. In this insightful blog, we’ll unveil practical tips tailored to safeguard your conveyor belt’s longevity. By implementing these straightforward strategies, you can avoid downtime and financial setbacks in the future.
Let’s embark on this journey to elevate your maintenance practices and secure the smooth operation of these indispensable components in the production process!
Common Conveyor Belt Problems
1. Tracking
The efficiency and reliability of conveyor belts depend on their ability to stay on track. Unfortunately, these systems often encounter belt mistracking and slippage, which can hamper productivity. Effective tracking is essential for ensuring smooth operation and high output.
Belt tracking involves managing and aligning the conveyor to ensure it stays on the correct path. Mistracking occurs when the belt slips to either side or becomes misaligned, leading to issues such as uneven wear and reduced belt life. In critical industries like food processing, mistracking can even trigger safety inspections.
The primary cause of mistracking is often material buildup on the underside of the belt or pulleys, which can lead to roller or pulley problems. Regular inspections and cleaning using dry steam-based solutions are crucial preventive measures to catch and address problems early.
2. Preventing Slippage
Maintaining precise tension in these systems is vital to prevent problems of slipping. Common causes of slippage include overweight loads, low temperatures, and pulley-related issues such as improper installation or malfunctions. Excessive tension can stretch the belt and cause it to slip, necessitating time-consuming maintenance.
Regular checks, cleaning, and repairs of these machines’ components can help avoid belt slippage issues.
3. Monitoring Material Carryback
Carryback refers to material that remains on the conveyor belt past the discharge point, leading to maintenance issues. Addressing carryback using primary and secondary cleaners, spray bars, and wash boxes is crucial for preventing roller and pulley problems and ensuring safety and productivity.
In environments where dry cleaning is necessary, using dry steam solutions and belt cleaners can effectively remove debris and maintain a clean and sanitized surface.
4. Preventing Seized Rollers
Conveyor belts, regardless of their material, can develop sharp edges when rollers seize up. Regular inspections of rollers are essential to prevent such occurrences, which can pose safety hazards and lead to costly repairs.
5. Repairing Tears and Seam Rips
Sharp-edged products can cause perforations and tears in conveyor belts, reducing their lifespan. Repair methods include vulcanization, metal fasteners, and cold curing. Vulcanization is a reliable but time-consuming process, while metal fasteners offer a quick fix but may not be as durable. Cold curing should be used when other options are not feasible.
7 Steps for Effective Conveyor System Maintenance
Enhancing the self-inspection process regularly and preparing for unforeseen repairs are essential for maximizing productivity and ensuring the reliability of conveyor systems. Here are seven steps to streamline conveyor maintenance and minimize the need for new belt installations:
1. Understand Specific Requirements
Facility managers must discern the unique maintenance needs of their establishments before tailoring maintenance programs and inspection protocols. For instance, the preventative maintenance regimen for a food processing plant conveyor system differs from that of a glass manufacturing plant.
2. Develop a Plan
A well-structured maintenance plan should outline procedures for equipment inspection, identification of preventative maintenance requirements, and a clear set of actions to address maintenance issues as they arise.
3. Implement Sanitation
Utilize approved wash-down cleaning chemicals for wet cleaning scenarios, while exploring the benefits of dry steam solutions for sanitizing surfaces in dry-clean-only environments.
4. Monitor Damage
Train technicians to meticulously inspect conveyor belts for signs of damage such as strings, frays, loose pieces, or general wear and tear on belts and components. These indicators signal the need for prompt repair or replacement.
5. Ensure Tracking
Verify that technicians install belts with the correct tension and maintain a debris-free environment around the conveyor system. Promptly address any tracking or alignment issues to prevent further damage.
6. Maintain Inventory
Minimize downtime by stocking essential spare parts like sprockets, drives, cleats, motors, and other critical components that are challenging to replace quickly.
7. Track Lifespan
Monitoring the lifespan of conveyor belts enables building operations and facility managers to devise a strategic replacement schedule. For instance, belts in a vegetable processing plant might necessitate daily replacement, while those in a distribution centre could last up to five years.
Analyzing this data allows technicians to identify mechanical issues in the conveyor system when belts start failing prematurely.
Preventive Maintenance Practices
Relying solely on reactive maintenance, where conveyor belt issues are addressed only when they break down, can lead to increased repair time, heightened downtime, and escalated maintenance costs.
It’s prudent to shift towards a preventive maintenance approach, where regular repairs are conducted to address potential issues before they escalate into major breakdowns. Integrating automation into your facility and establishing key indicators to signal when specific equipment requires maintenance can streamline this process.
For instance, detecting an overheating boiler allows for timely thermostat repairs, preventing system-wide halts. Develop a robust maintenance program focused on early issue identification and prompt resolution. This program stresses recommended service schedules, with regular inspections and ongoing belt performance assessments.
Maintenance and Repairs
Maintaining thorough documentation of conveyor maintenance and repairs is instrumental in identifying consistently problematic parts and equipping workers with the necessary knowledge to detect trouble signs. Such documentation aids in expediting diagnoses during emergencies, thereby minimizing downtime.
Consider enhancing maintenance efforts by incorporating sensors into conveyors and integrating artificial intelligence for predictive maintenance. Installing suitable software programs can significantly enhance the efficacy of predictive maintenance initiatives leveraging AI and machine learning.
FAQs: 7 Conveyor Belt Maintenance Tips with Long-Lasting Effects
What are the daily checks to maintain a conveyor belt?
Daily checks involve inspecting for wear, tears, debris, and unusual noises. Ensure proper tension and tracking, and address any issues promptly to maintain optimal operation.
How long do conveyor belts last?
Conveyor belt lifespan varies based on usage, maintenance, and environment. With proper care, they can last from 2 to 20 years, depending on factors like material and workload.
Which material is best for a conveyor belt?
For conveyor belts, materials like rubber, PVC, and polyurethane are common choices. Selection depends on factors such as load, speed, and environment to ensure durability and efficiency.
What kind of oil is best for conveyor belts?
Silicone-based lubricants are often recommended for conveyor belts due to their resistance to water, temperature fluctuations, and compatibility with various belt materials.
How often should conveyor belts be cleaned?
Conveyor belts should be cleaned regularly, ideally daily or weekly, depending on usage and material handled. Cleanliness prevents debris buildup, reducing wear and contamination risks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, prioritizing effective conveyor belt maintenance is paramount for sustaining seamless operations in industrial settings. By implementing proactive measures outlined in this guide, such as regular inspections, etc. facilities can ensure prolonged conveyor belt longevity and minimize costly disruptions.
Leveraging advanced technologies like predictive maintenance further enhances efficiency and reduces downtime. As industry leaders, consider partnering with Qodenext for innovative solutions to streamline conveyor belt maintenance, ensuring sustained productivity and reliability for years to come.