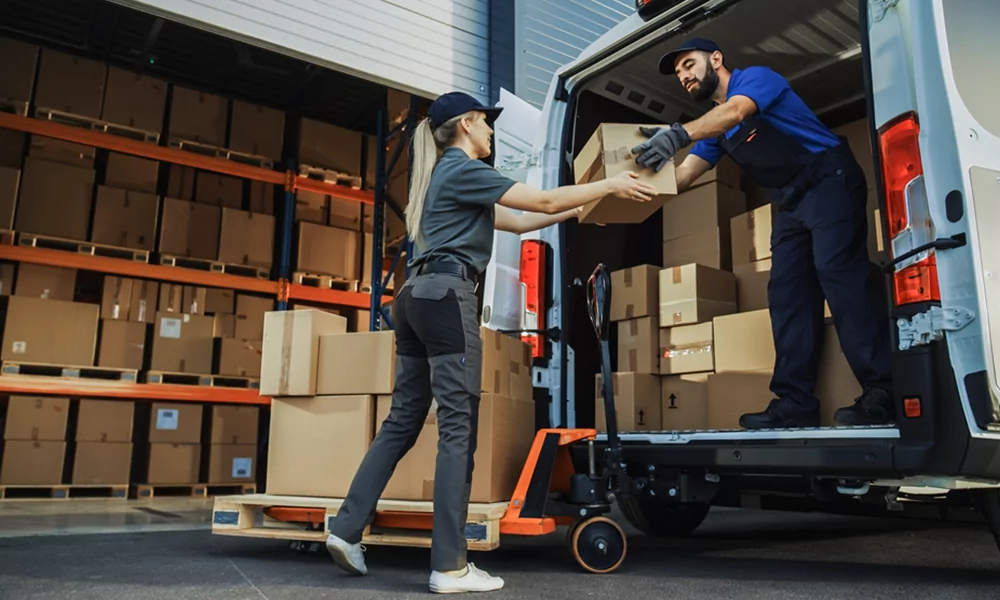
Unlocking the potential of reverse logistics is pivotal for modern businesses seeking to thrive in the competitive landscape of e-commerce. With returns accounting for a substantial portion of sales and processing costs, it’s imperative to view them not just as setbacks but as avenues for growth and optimization. In this guide, we unveil five essential strategies on How to improve reverse logistics framework, spanning from automation to elevating the customer experience. Leverage these insights to streamline operations and boost efficiency in handling returns, driving sustainable success in the digital marketplace.
Let’s begin by first by defining the term reverse logistics.
Defining Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics is the essential supply chain mechanism responsible for returning products from end users back through the supply chain to either the retailer or manufacturer.
Whether initiated by customers returning unnecessary items, reaching the end of a product’s life cycle, or encountering damaged or flawed products, facilitating returns is fundamental for business operations. Reverse logistics encompasses not only product returns but also disposal or recycling needs.
Additionally, it involves scenarios where end users handle refurbishment, disposal, or resale of the product. This process ensures efficient management of product flows in the reverse direction, optimizing resources and customer satisfaction.
Importance of Reverse Logistics
In a supply chain management, this is one of the most important aspects. Let’s look at why it is this way:
1. Returns Policy
Every selling company benefits from having a comprehensive returns policy in place. Embracing returns enables customers to rectify mistaken purchases or select the correct specifications, enhancing their satisfaction and loyalty to your brand.
2. Rented Items
Certain companies offer rental services for their products with predefined rental periods and return expectations. It’s crucial to clearly communicate the return process at the end of the rental term.
3. Repairs
In the event of a product malfunction within a specified timeframe, manufacturers often provide repair services, provided the item wasn’t misused. Maintenance services may also be offered to ensure products remain in optimal condition.
4. Refurbishing / Rebuilding
Clients upgrading to newer product versions may trade in older models, which can be refurbished for resale or dismantled for repurposing materials.
5. Delivery Issues
Transportation mishaps, such as missed deliveries or unforeseen delays, may necessitate returning goods to the warehouse as the only viable solution.
6. Recycling
Reverse logistics are vital for managing end-of-life products. Some manufacturers offer recycling programs to collect and repurpose materials from discarded items.
Benefits of Reverse Logistics
The return process constitutes a fundamental aspect of selling products or materials. Customers expect the flexibility to return items that don’t meet their needs, are defective, or have reached the end of their usefulness.
While it might be tempting to improvise the returns process, doing so could have detrimental effects on your business. Even products deemed faulty or recalled often retain some residual value.
Moreover, both current and potential customers closely observe how returns are managed, underscoring the importance of investing resources into an efficient reverse logistics system. Here are six compelling benefits of such an investment:
1. Cost Reductions
Efficient reverse logistics can yield substantial cost savings across various operational facets. By implementing optimized processes and engaging competent stakeholders, expenses related to transportation, administration, repairs, tech support, quality assurance, marketing, and disposal can be minimized.
Tracking the total cost of ownership for each product category enables you to gauge the effectiveness of your cost-saving measures, ultimately bolstering your bottom line.
2. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Fostering customer loyalty is paramount to achieving business objectives, with research indicating that approximately 96% of consumers are inclined to repeat purchases if they have positive return experiences.
Prioritizing customer happiness in return transactions can be achieved through initiatives such as offering free return shipping, providing full refunds sans restocking fees, and dispensing with the requirement for original packaging returns.
3. Elevated Brand Reputation
Customer perception of your brand is heavily influenced by how adeptly returns are handled. A lenient return policy that prioritizes customer satisfaction can significantly enhance brand reputation and attract new clientele. Conversely, a reputation for obstructive returns processes may deter potential customers.
4. Risk Mitigation
A robust reverse logistics system incorporates risk assessment strategies, particularly concerning product exchanges and disposal. Factors such as safety recalls or sensitive data disposal necessitate meticulous handling to mitigate associated risks effectively.
5. Sustainable Practices
Contrary to common belief, not all items returned through the supply chain are destined for disposal. Many can be repurposed or reused, thereby prolonging their lifespan and diverting them from landfills.
Implementing recycling initiatives, particularly for electronics, not only minimizes environmental impact but also enhances brand image through sustainable practices.
6. Increased Profitability
Optimizing reverse logistics can significantly bolster profitability by unlocking revenue streams from returned items. Many returned products, albeit unsuitable for the original purchaser, remain in pristine condition for resale.
A streamlined reverse logistics process facilitates hassle-free returns, inspections, repairs, and subsequent reintroduction of items into inventory, contributing to enhanced profitability through secondary market opportunities.
Establishing Robust Reverse Logistics Processes
There are certain ways to establish reverse logistics, we’ve mentioned a few below:
1. Document
Develop comprehensive workflows, KPIs, and best practices specific to reverse logistics. Highly skilled employees already proficient in these processes should lead training and onboarding for new staff members.
2. Key Steps and KPIs
Identify critical steps such as traffic distribution, intake speed, and product verification. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should measure efficiency in these areas, including peak return days, intake speed, and accuracy of product verification.
3. Dedicated Team
Allocate specialized resources to handle reverse logistics, recognizing its impact on financial KPIs. A dedicated team ensures efficient identification, sorting, and handling of returned goods, ultimately benefiting customer fulfillment rates.
4. Prioritize Customer Experience
Streamline the returns process to enhance customer loyalty. Minimize inventory cycle time and improve dock-to-stock efficiency to promptly credit customers for returned merchandise. Provide transparent tracking and progress reports to optimize returns and ensure customer satisfaction.
5. Implement Control
Integrate quality control processes with reverse logistics to identify defects and issues. Utilize standardized inspection guides to verify contents and assess manufacturing quality upon receipt of returned products.
6. Embrace Practices
Enhance environmental sustainability by optimizing reverse logistics processes. Reduce waste and environmental footprint by implementing reuse, resale, and recycling initiatives, aligning with eco-conscious consumer preferences and enhancing corporate reputation.
7. Provide Transparency
Ensure transparency across both forward and reverse logistics processes. Track performance throughout the product lifecycle to identify areas for improvement and optimize supply chain operations holistically.
8. Communicate Policy
Clarify the returns policy to facilitate ease for customers. Clearly state the returns process and timelines, providing step-by-step guides to minimize delays and ensure returned items are received in good condition, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
FAQs: How to Improve Reverse Logistics: 8 Amazing Tips
What risks are there in reverse logistics?
Risks in reverse logistics include mishandling of returned items, data security breaches, disposal liabilities, and potential losses from unsalvageable products or fraudulent returns.
What are the 5 R’s in reverse logistics?
The 5 R’s in reverse logistics are Return, Recall, Repair, Refurbish, and Resale, representing the key stages in managing returned goods.
How many types of reverse logistics are there?
There are two main types of reverse logistics: post-consumer returns, involving products returned by end-users, and post-sale returns, involving products returned from distribution channels.
Does reverse logistics reduce waste?
Yes, reverse logistics reduces waste by facilitating reuse, recycling, and proper disposal of returned products, diverting them from landfills and promoting environmental sustainability.
What is an example of reverse logistics?
An example of reverse logistics is a company collecting used electronic devices from customers, refurbishing them, and reselling them or recycling their components for reuse.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering reverse logistics is indispensable for modern businesses aiming to thrive in the digital era. By implementing the five essential strategies on how to improve reverse logistics, companies can streamline operations, reduce costs, enhance customer satisfaction, and promote sustainability.
With a robust reverse logistics framework in place, businesses can efficiently manage returns, minimize waste, and capitalize on revenue opportunities. To further optimize reverse logistics and unlock its full potential, consider partnering with Qodenext, a leading provider of innovative supply chain solutions.